Computer monitor buying guide: A comprehensive breakdown from resolution to color!
There are numerous and intricate parameters for computer monitors, and with so many monitor brands in the market, how do we choose? Today, let's delve into the various parameters of computer monitors.
Monitor Size
Monitor size refers to the length of the diagonal of the monitor screen, measured in inches. Common monitor sizes include 21.5 inches and below, 22-26.9 inches, 27 inches, 28-32 inches, and above 32 inches. It's important to note that bigger isn't always better when it comes to monitors, unlike TVs. Monitors are typically used from a close distance, so imagine how overwhelming a very large monitor would be right in front of you!
A monitor with a screen too small is definitely not ideal, but one that's too large can also be problematic, making it difficult to take in the entire screen, especially during work or gaming (except for special needs like multi-screen setups for split-screen work or stock market monitoring). The primary reason is the limited range of eye focus, coupled with the need to maintain a certain working area (larger sizes also consume more space). For most users: a 24-inch 16:9 monitor is ideal for office work, while 24/27-inch monitors are suitable for gaming, as they are easily available, with ample supply in this range and relatively affordable prices.
Monitor Resolution
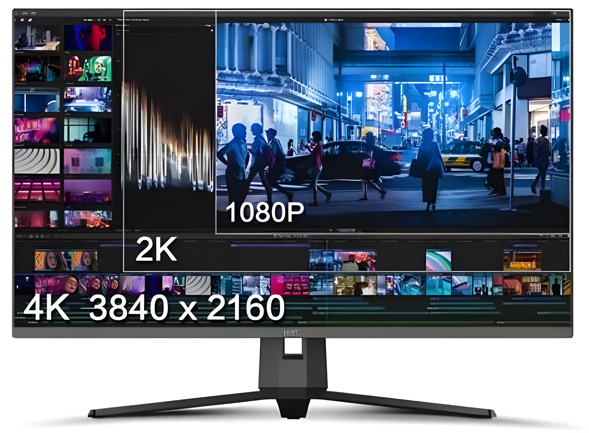
Resolution refers to the number of pixels per unit area. With the same screen size, a higher resolution results in a more detailed, clearer, and vibrant display. However, higher resolutions also consume more graphics card resources, so it's necessary to consider the support level of your graphics card.
1080P/FHD:1920 * 1080
2K/QHD:2560 * 1440
4K/UHD:3840 * 2160
8K/UHD:7680 * 4320When selecting a monitor's resolution, it's crucial to consider the maximum resolution supported by your graphics card. Otherwise, you might end up with a 4K resolution monitor that your graphics card can't handle effectively. Given that most graphics cards can support 2K resolution, when purchasing a 24"/27" monitor, it's recommended to start with 2K resolution, which offers a higher pixel density, allowing for a larger display area and a more refined viewing experience.
Monitor Refresh Rate
Screen refresh rate refers to the number of times the electron beam scans and refreshes the image on the screen per second. Simply put, it's how many times the screen is updated with new images in one second. A higher refresh rate results in a more stable display with smoother transitions between frames. High refresh rates significantly reduce screen tearing and latency, making them especially important for gamers. Common refresh rates in the market range from 60Hz-120Hz, 144Hz-170Hz, 170Hz-240Hz, and above 240Hz.
However, a higher refresh rate isn't always necessary. For basic office work or watching movies, 60Hz-120Hz is generally sufficient. If you enjoy FPS games, 144Hz-170Hz should be more than enough. Above 170Hz is mainly suitable for professional needs such as game development and 3D modeling.
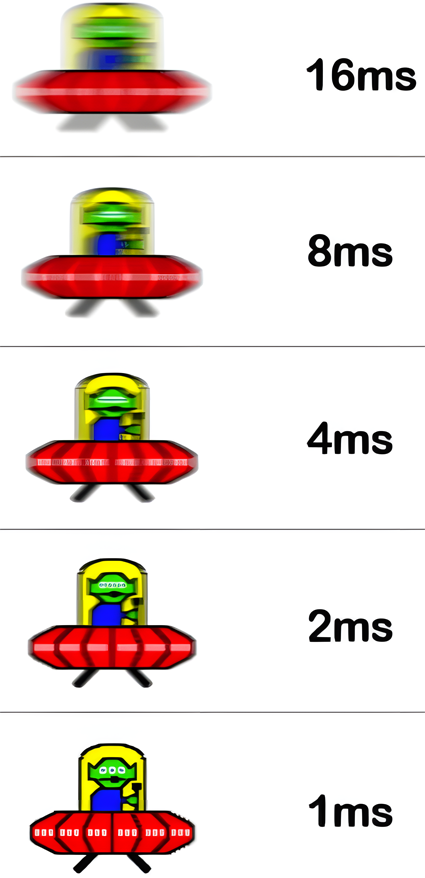
Monitor Response Time
Currently, the response time specified for monitors is mostly the grey-to-grey (GTG) response time. Measured in milliseconds (ms), it indicates how long it takes for a pixel to change from one color to another. A shorter response time means less ghosting, higher image clarity, and smoother motion. The fastest response time for gaming monitors is currently 1ms, while mainstream gaming monitors fall within the 2ms-5ms range, which is generally sufficient. OLED displays boast an even faster response time of 0.1ms.
The typical response times for monitors range from 0.5ms, 1ms, 2ms-4ms, to 5ms and above. For gaming, 0.5ms-2ms is sufficient, while 2ms-4ms is ideal for home and office use.
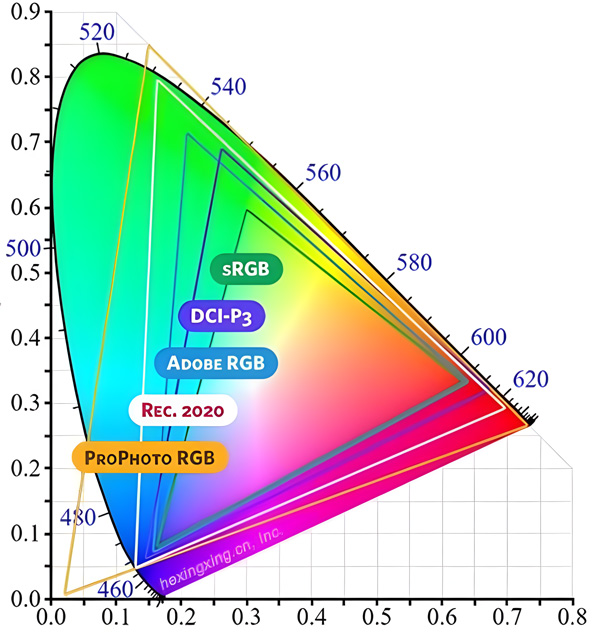
Monitor Color Gamut
Color gamut represents the color range (color coverage) that a monitor can display. A wider color gamut means the monitor can reproduce more colors, resulting in more vivid and realistic images. There are five major color gamut standards: sRGB, Adobe RGB, NTSC, and DCI-P3. Most monitors today adopt 100% sRGB (equivalent to 75% NTSC), which is suitable and economical for most users. For movie and TV series enthusiasts, sRGB is recommended for its rich color reproduction. For professional office work, NTSC is preferred for its more realistic image quality.
Monitor Color Depth
Color depth, also known as bit depth, refers to the number of colors a monitor can display, affecting the smoothness of color transitions. The higher the color depth, the smoother and richer the color transitions appear. Currently, monitor color depths mainly include 6bit (2^6=64 colors), 8bit (256 colors), 10bit (1024 colors), and 12bit (4096 colors). Generally, VA panels can only reach up to 8bit, while IPS panels can achieve 10bit or even higher. Therefore, IPS screens are highly recommended.
Apart from high resolution, most Apple devices feature higher color depths, resulting in exceptionally smooth and natural visual transitions without distinct boundaries, contributing to the comfortable viewing experience of Apple's iPad and Mac.
Monitor Color Accuracy
Color accuracy, measured by the △E value, indicates the degree of difference between the colors displayed by the monitor and the actual colors of objects. A lower △E value signifies higher color accuracy. To meet the stringent requirements of professional photographers and image workers, monitors are typically required to have a △E ≤ 2. Consumer-grade monitors, with △E values ranging from 3 to 12, suffice for activities such as browsing the internet, gaming, and watching videos.
Monitor Screen Brightness
Screen brightness is measured in nits. Neither extreme brightness nor excessive dimness is ideal; comfort for the human eye is key. If the monitor is placed near a window, excessively low brightness can result in a dim screen, while overly bright screens can strain the eyes. Moderate brightness is recommended for office work, promoting comfort and enhancing productivity.
Monitor Screen Contrast Ratio
Contrast ratio refers to the ratio of the brightest to the darkest points on the screen at the same location. A high contrast ratio indicates relatively higher brightness and more vibrant colors. Typically, the contrast ratio mentioned refers to static contrast, which is the number of levels between white and black in an image. A higher static contrast ratio translates to more levels from white to black, resulting in brighter and more vivid images.
HDR Function
HDR (High-Dynamic-Range) technology provides a broader range of brightness and colors, enabling images to more closely resemble real-world visuals. In the realm of imaging, dynamic range refers to the difference between the brightest and darkest parts of an image. A larger dynamic range captures richer details in both the brightest and darkest areas of an image. While HDR's impact in daily use may be subtle, it is crucial in gaming environments, enhancing the realism and detail of game visuals.
Current HDR standards include HDR10, HDR400, HDR600, HDR1000, HDR1400, and HDR2000.
Monitor Panel Types
The panel is the heart of an LCD monitor, accounting for approximately 80% of its cost. There are several mainstream panel types in the market today: IPS, VA, OLED, and Mini-LED.
- IPS Panel: With relatively high manufacturing costs, IPS panels are priced higher. They are currently the mainstream and popular choice due to their rich colors, wide viewing angles, top-notch image quality, high brightness, and moderate response speed. Therefore, they are often used in office computers for professional technical processing. However, light leakage in IPS panels is quite common and unavoidable. Generally, as long as the light leakage is not exaggerated to the point of being visible to the naked eye, it is considered normal. The rapid development of IPS technology has led to the emergence of Fast-IPS, tailored for gaming, and Nano-IPS, which balances gaming and image quality.
- VA Panel: Featuring lower manufacturing costs, VA panels are more affordable. They offer high contrast ratios when viewed straight on and decent viewing angles, albeit slightly inferior to IPS. However, VA panels are prone to uneven color display, which can only be optimized through software by individual brands. Currently, VA panels are mostly used in curved monitors.
- Mini-LED Panel: Traditional LCD monitors consist of an outer panel and backlight behind it, with the panel responsible for displaying colors and the backlight for emitting light. Mini-LED refers to the backlight, while the panel itself remains the familiar IPS or VA type. Due to their high manufacturing costs, Mini-LED monitors are priced relatively high.
- OLED Panel: OLED represents an independent system and a brand-new technology that does not rely on the traditional backlight + panel configuration. With a simple structure, OLED panels are much thinner than traditional LCDs and boast extremely fast response speeds. However, their complex technology leads to high manufacturing costs and expensive prices.
Color & Color Accuracy: OLED > Mini-LED > IPS > VA
Response Speed: OLED > Mini-LED > IPS > VA
Viewing Angle: OLED > Mini-LED, IPS > VA
Contrast Ratio: OLED > Mini-LED > VA > IPS
Brightness: Mini-LED > OLED
Price: OLED > Mini-LED > IPS > VAMonitor Interfaces
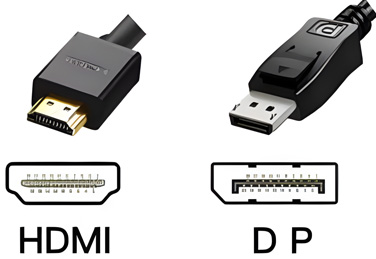
Monitor interfaces are often overlooked when selecting a monitor. The main interfaces include HDMI, DisplayPort (DP), Type-C, USB, VGA, and DVI. VGA and DVI interfaces are gradually being phased out and are only found on some low-end or special-function monitors. For those requiring high-definition image quality, at least one of HDMI or DP is necessary.
tags:
Must-read for gamers! Buying guide for high-performance gaming monitors
Blessing for office workers: How to choose an eye-friendly and comfortable computer monitor?
Exclusive for designers: Shopping tips for color-accurate professional monitors
Cost-effective choice: High-quality computer monitors available within a limited budget










Comments (0)