Necessary for computer upgrade! How to choose the most suitable computer memory for you?
What is Computer Memory?
Memory, situated between the CPU and the hard disk, is a crucial component of a computer that functions as a high-speed read-write storage device. The CPU processes data at an incredibly fast pace, whereas the hard disk's read-write speed is relatively slow, unable to keep up with the CPU's demands. Therefore, the computer retrieves data from the hard disk and stores it in the memory, allowing the CPU to directly access it when needed. After processing, the data is returned to memory before ultimately being written back to the disk.
Memory DDR Generations
Currently, the main DDR generations include DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, with DDR5 being the mainstream and DDR6 poised for release. Higher DDR generations offer higher frequencies and bandwidths but come with a higher price tag. Before making a selection, it's crucial to check the maximum DDR generation supported by your CPU and motherboard.
Memory Frequency
In general, memory frequency refers to the speed of data transfer. A higher frequency translates to better performance but also a higher price.
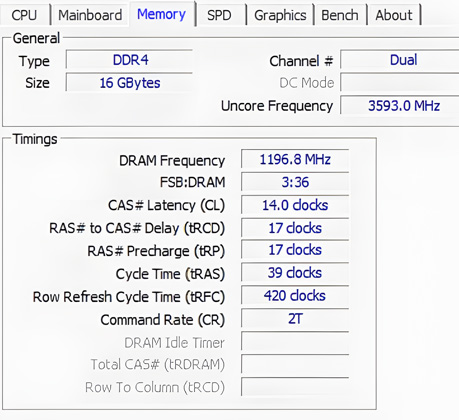
Memory Timings
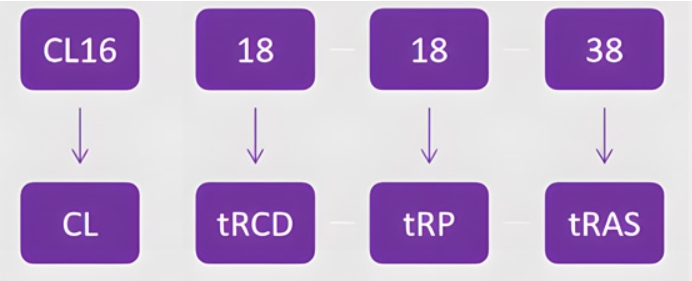
Memory timings (RAM timings) are four parameters describing the performance of Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (SDRAM): CL, TRCD, TRP, and TRAS, measured in clock cycles. They are typically written as four numbers separated by dashes, such as 16-18-18-38. Memory timings indicate the memory's response time—how long it takes for the memory to react after receiving a command from the CPU. In simple terms, lower timings represent shorter latency, allowing for faster memory response.
Memory Latency = Timings (CL x 2000) / Memory Frequency, measured in nanoseconds (ns).With the same frequency, lower timings result in lower latency. Conversely, with the same timings, a higher frequency also leads to lower latency.
CL(CAs Latency): It is the delay time, measured in clock cycles, that a memory module requires to access and return data in response to a read command from the CPU. A lower CAS Latency indicates faster memory response and can contribute to improved overall system performance.
tRCD(RAS to CAS Delay): It is the delay between the activation of the Row Address Strobe (RAS) signal and the Column Address Strobe (CAS) signal in memory operations. It represents the time required for the memory to transition from selecting a row address to selecting a column address, and is a critical timing parameter that affects memory performance.
tRP(RAS Precharge Time): It is the time interval between the end of one row access and the beginning of the next in memory operations. Specifically, it represents the duration that must elapse after a precharge command is issued before a new row can be activated, which is a crucial aspect of memory timing that affects performance.
tRAS(RAS Active Time): It is a crucial timing parameter in memory operations that refers to the duration of time that a row in memory remains active before it must be precharged for reuse. Specifically, it measures the minimum period from when a row is activated (by asserting the Row Address Strobe, or RAS, signal) to when it must be precharged in preparation for a new access, thus affecting the overall efficiency and performance of memory transactions. This parameter plays a significant role in optimizing memory access patterns and minimizing delays in data retrieval.
How Much Memory Capacity is Suitable?
The memory capacity directly impacts the amount of data it can store. While it's always good to have ample memory capacity, having more than necessary is meaningless as it leads to resource wastage, unless money is no object.
- 8GB: Sufficient for routine tasks such as office work, browsing the internet gaming, light, watching videos, etc.
- 16GB: Sufficient for most demanding tasks like playing high-end games, video editing, graphic rendering, etc.
- >=32GB: Suitable for specialized needs such as modeling and rendering.
Memory Stick Appearance
Currently, there are two main types of memory sticks: heat spreader sticks and regular sticks. Heat spreader sticks, also known as armored sticks, feature an additional metal shell on top of a regular memory stick. This metal shell, often a metal plate, aims to improve the heat dissipation and shock resistance of the memory stick. By enhancing heat dissipation, it also offers better overclocking potential. Regular sticks, also called conventional memory sticks, are those without an extra metal shell. They have a simple appearance with the PCB board directly exposed, lacking additional heat dissipation or shock resistance measures. Consequently, heat spreader sticks tend to be more expensive than regular sticks of the same brand, specifications, and capacity. Users can choose according to their needs.
What are Some Memory Brands?
Common memory brands include Kingston, Samsung, Hynix, and A-Data. Among them, Kingston is known for its excellent compatibility.
What is Dual-Channel Memory?
Dual-Channel Memory Technology is essentially a memory control and management technique that relies on the memory controller of the chipset. Theoretically, it doubles the bandwidth provided by two memory modules of the same specifications. Therefore, dual-channel has advantages over single-channel in terms of reading and writing speed, resulting in significantly faster performance when opening software or documents in daily use. Simply put, if we compare memory to a highway between the CPU and the hard disk, then single-channel memory can be likened to a single-lane highway, whereas dual-channel memory would be a two-lane highway, offering higher transmission efficiency. Correspondingly, there is also quad-channel memory, but it is only supported by relatively high-end motherboards.
Can Dual-Channel Memory Have Different Frequencies?
Dual-channel memory can have different frequencies, but the memory with the higher frequency will automatically downclock to match the frequency of the lower one.
Why is it Recommended for Overclockers to Buy Memory Kits?
Due to the manufacturing process of chips, it cannot be guaranteed that every memory chip performs identically. When two memory modules are used together, there may be some compatibility issues. Memory kits, on the other hand, are typically produced in the same batch, resulting in much better compatibility. While manufacturers' technologies have advanced, ensuring that memory modules from different batches can work together without major issues, it is not always guaranteed that they will function flawlessly during overclocking. Therefore, overclockers are advised to purchase memory kits, which are generally more expensive than buying two separate memory modules.
tags:
Comprehensive Guide! How to Choose the Best Computer RAM for You
Essential for PC Upgrade! Memory RAM Selection Tips and Considerations
Must-read for Gamers! Secrets to Picking High-Performance Computer RAM
On a Budget? Guide to Selecting Cost-effective High-performance Computer RAM







Comments (0)